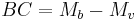Bolometric correction
In astronomy, a bolometric correction is a correction that must be made to the absolute magnitude of an object in order to convert an object's visible magnitude to its bolometric magnitude. Mathematically, such a calculation can be expressed:
The following is subset of a table from Kaler[1] (p. 263) listing the bolometric correction for a range of stars. For the full table, see the referenced work.
| Class | Main Sequence | Giants | Supergiants |
|---|---|---|---|
| O3 | -4.3 | -4.2 | -4.0 |
| G0 | -0.10 | -0.13 | -0.1 |
| G5 | -0.14 | -0.34 | -0.20 |
| K0 | -0.24 | -0.42 | -0.38 |
| K5 | -0.66 | -1.19 | -1.00 |
| M0 | -1.21 | -1.28 | -1.3 |
The bolometric correction is large both for early type (hot) stars and for late type (cool) stars. The former because a substantial part of the produced radiation is in the ultraviolet, the latter because a large part is in the infrared. For a star like our Sun, the correction is only marginal because the Sun radiates most of its energy in the visual wavelength range.
See also
External links
- http://www.peripatus.gen.nz/Astronomy/SteMag.html - contains table of bolometric corrections
- http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1996ApJ...469..355F/0000360.000.html - contains a detailed table of bolometric corrections
References
- ^ Kaler, James B. (1989). Stars and their spectra: An Introduction to the Spectral Sequence. pp. 300.